Supplier Relationship Management and Third-Party Risk Management Model
In this issue
12 March 2020:
Supplier Relationship Management and Third-Party Risk Management Model
Introduction
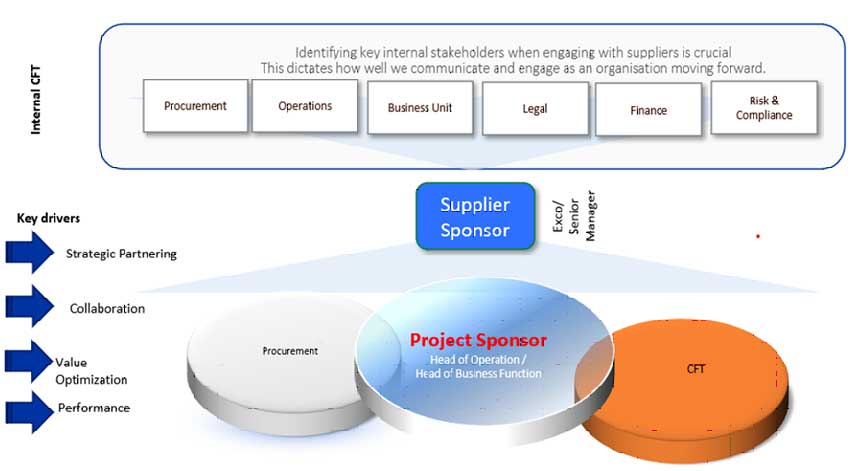
In our interactions with clients we find that organisations have a very one-dimensional approach to Supplier Relationship Management (SRM). We find the value of SRM is focused only on cost reduction and SLA management.
This blog is focused on the implementation approach that was followed in Project Ignite to introduce and embed the principles of SRM.
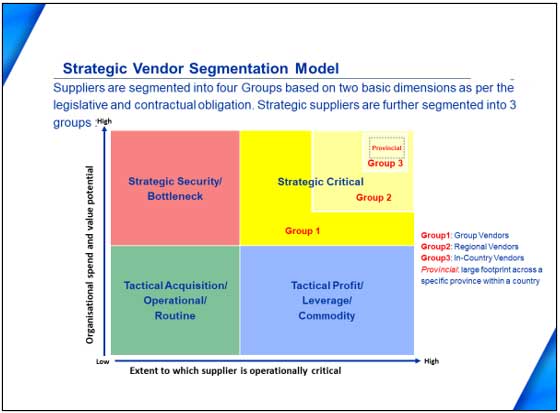
SRM and Risk Segmentation Model
Summary
To secure the suppliers commitment to the relationship and continuous high service delivery, reward programs such as Supplier Compliance Certificate or Supplier Recognition can be implemented within the SRM Plan.
There are Several benefits associated with supplier relationship management, and they all culminate in a healthier bottom line as we saw in Project Ignite.
janineh@tkjprocurement.com | etienneh@tkjprocurement.com | www.tkjprocurement.com